No products in the cart.






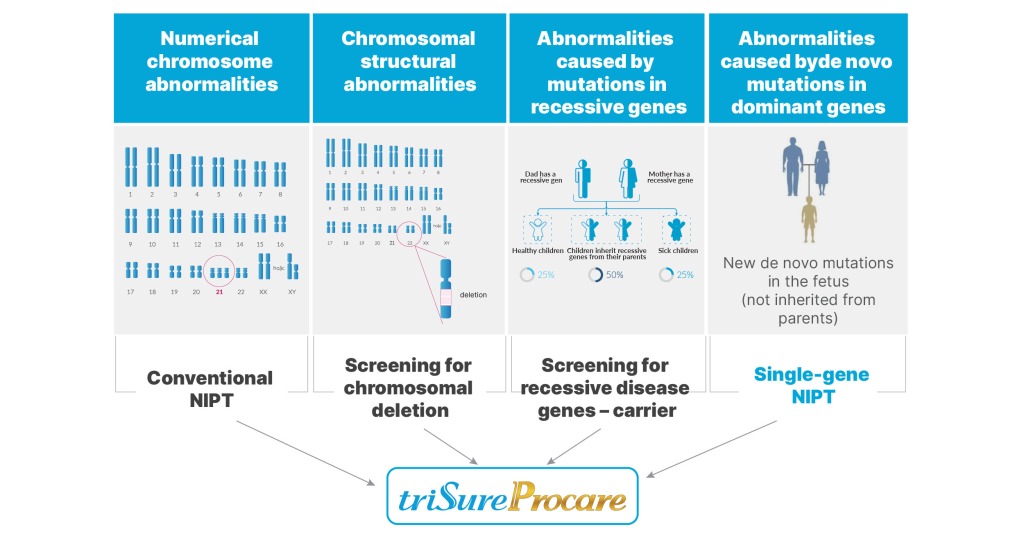
The first prenatal screening test for dominant single-gene inherited disorders in Vietnam, the NIPT test detects 25 of the most common dominant single-gene inherited diseases – which have a cumulative frequency higher than Down syndrome – with just one maternal blood draw.
These are serious diseases that affect the quality of children’s lives, but cannot be detected by conventional NIPT testing or screening for recessive disease genes (carrier). Early screening within nine weeks’ gestation will help timely intervention and effective newborn treatment, or a better pregnancy management plan.
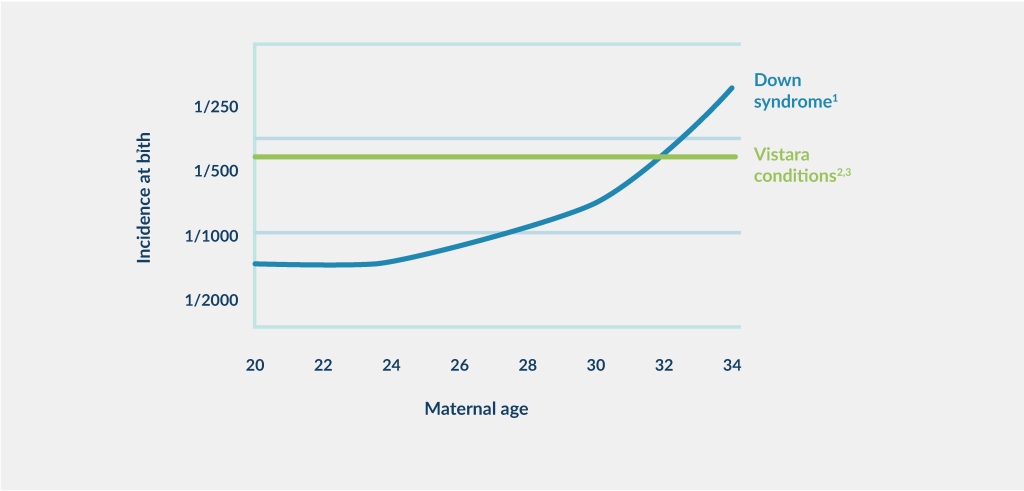
60 percent of severe single-gene diseases after birth are caused by de novo mutations in the foetus (inherited from neither parent)1
De novo mutations in the foetus increase with paternal age (not related to maternal age), i.e. the older the father (>40 years old), the greater the risk of having a child with a dominant genetic disease caused by a de novo mutation(2).

Achondroplasia, hypochondroplasia, lethal skeletal dysplasias, brittle bone disease, CATSHL syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.

Muenke syndrome, Crouzon syndrome, Antley Bixler syndrome, Apert syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome, Jackson Weiss syndrome.

Noonan syndrome, Leopard syndrome, Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome

Alagille syndrome, Charge syndrome, Cornelia de Lange syndrome, Costello syndrome, childhood epilepsy, intellectual disability, juvenile myelomonocytic leukaemia, Rett syndrome, Sotos syndrome, Tuberous sclerosis.









Copyright © 2020 GENE SOLUTIONS
Legal Representative: Nguyễn Hữu Nguyên
Enterprise No. 0314215140 – HCMC D.P.I issued on January 23, 2017
GET MEDICAL CONSULTATION FROM DOCTORS
Tư vấn di truyền